Windows Registry is the core of Windows operating system. It is a database containing specified configuration settings to processes, services, applications, and Windows components. The behavior of all these elements can be modified through editing their concerned registry entries.
For common PC issues, Junk files unclogging, boosting System performance, speeding up Internet and other underlying Windows concerns, we recommend using this tool.
- Step 1 : Download Systimizer ‒ PC Cleaner & Internet Booster (Effective with Windows 10, 8, 7 & XP)
- Step 2 : Click "Scan" to analyze your PC
- Step 3 : Click "Fix" to wipe out all bumps
As opening and editing Windows Registry is a sensitive thing to do, it is always recommended to proceed with certain cautions. This article aims to educate you in the same regard. Here, you will find out the possible ways to access Registry Editor in a number of Windows operating systems.
Designated underneath, are the methods to contact Windows Registry Editor, in Windows XP, Vista, 7, and 8 (8.1), sequentially.
Opening Registry Editor in Windows XP
Windows XP inherited Registry Structure from Windows 95 and 98. As similar to those operating systems, XP has the ability to Edit, Backup, and Restore the Windows Registry. The most common way to access and edit Registry database in Windows XP is described in the procedure beneath.
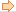
- Click Start button or Press Windows key, to open the Start menu
- Choose Run option in the Start menu, to open the Run dialog box
- Alternatively, press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box
- Type ‘regedit’ in the Run dialog box, and hit Enter
- Then opens the Registry Editor
Opening Registry Editor in Windows Vista/Windows 7
Windows 7 and Windows Vista have quite a resemblance among them, and share many common attributes. Access to Windows Registry Editor also points towards a similar direction in both the operating systems. That is the reason; both of them are mentioned under the same caption. Follow these steps to contact Registry Editor, if you are a Windows 7 or Vista user.
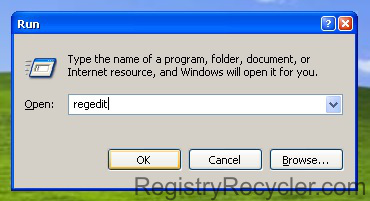
- Click Start button or Press Windows key, to open the Start menu
- Click inside the Search bar, within the Start menu
- Type ‘regedit’ in the Search box, and hit Enter
- A UAC (User Account Control) message alert would prompt you to confirm your action
- Proceed with Yes, to open the Registry Editor
- Or, press Windows key + R to open Run dialog box
- Type ‘regedit’ in the Run box and hit Enter
- Click Yes, if prompted with UAC message box, to open Registry Editor
Note: Administrator Mode or UAC is a security feature that protects important OS locations and operations against accidental and malicious modifications. It can also be protected by a password.
Opening Registry Editor in Windows 8 and 8.1
As Windows 8 has introduced a completely modernized user interface, it may trouble the users in finding a way to Registry Editor. It is obvious that the subject technique in Windows 8 is absolutely different from that in older versions as there is no Start menu. If you are a Windows 8 (8.1) user, wanting to edit your Windows Registry, it is advised to do as directed below.
You are hereby informed that the practice to access Registry Editor is similar for both Windows 8 and Windows 8.1.
- If you’re on Windows 8 Desktop screen, point your cursor in the upper right corner of screen
- In the appearing Charm bar, click on the Search icon to display a Search box
- If you are on Start screen, you can just start typing and it would appear in Search box
- Type ‘regedit’ in the Search box, and make sure the Apps tile is selected below the Search box
- In the Search results on the left side, click to open regedit
- Click Yes, if prompted with UAC dialog box, to open Registry Editor
- Or, press Windows key + R to open Run dialog box
- Type ‘regedit’ in the Run box and hit Enter
- Click Yes, if prompted with UAC message box, to open Registry Editor
Editing Registry through Registry Editor
You can change the settings and behaviors of your operating systems by editing certain keys, values, and data of Windows Registry. A proper way to edit these characteristics of Windows Registry is mentioned below in a sequential order.
- To reach a destined key, navigate through the Registry tree under Computer node, in the left panel of Registry Editor
- To add a New Key, right click the key under which you want to create a key, go to New and choose to create a new key
- To Remove a Key, right click the desired key and choose Delete. Confirm the prompt message
- To create a New Value, right click the key that you want to contain the new value, go to New and select among the values in the list
- To Modify the data within a value, double click the Value name and replace the Value data with desired value
- To Remove a Value, right click the Value name, choose Delete and confirm your action
- To create a Backup of Registry, go to File menu, select Export, choose All under Export range, and save it with a desired name.
- To Restore a state of Registry, go to File menu, select Import, and select any previously created backup from a directory


 Tailor Your Own Windows 8 Start Screen
Tailor Your Own Windows 8 Start Screen